ESET Analysis
One of the crucial superior server-side malware campaigns continues to be rising, with a whole lot of hundreds of compromised servers, and it has diversified to incorporate bank card and cryptocurrency theft
14 Might 2024
•
,
3 min. learn

Ten years in the past we raised consciousness of Ebury by publishing a white paper we known as Operation Windigo, which documented a marketing campaign that leveraged Linux malware for monetary achieve. Right this moment we publish a follow-up paper on how Ebury has developed, and the brand new malware households its operators use to monetize their botnet of Linux servers.
The arrest and conviction of one of many Ebury perpetrators following the Operation Windigo paper didn’t cease the botnet from increasing. Ebury, the OpenSSH backdoor and credential stealer, was nonetheless being up to date, as we reported in 2014 and 2017.
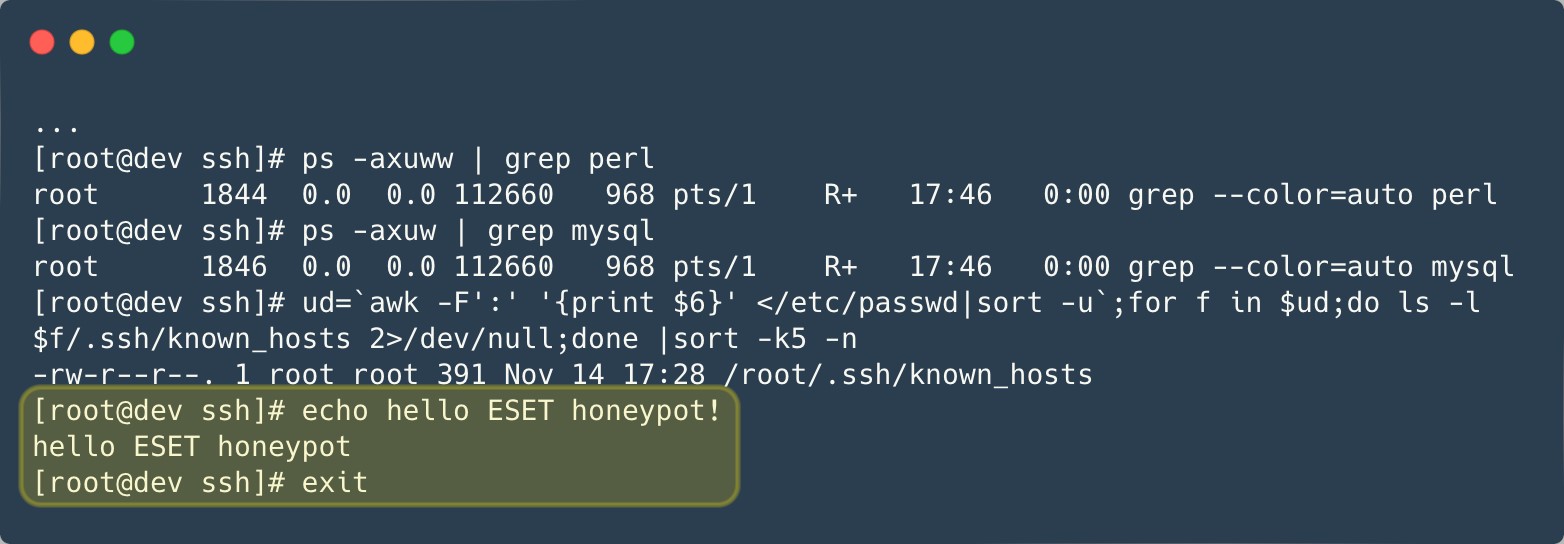
We keep honeypots to trace new samples and community indicators. Nonetheless, it has change into increasingly tough to run such honeypots as Ebury developed. For example, considered one of our honeypots didn’t react precisely as anticipated when Ebury was put in. After spending hours making an attempt to debug what was occurring, Ebury operators lastly deserted the server and despatched a message to point out that they knew about our makes an attempt at tricking them, as proven in Determine 1.
In 2021, the Dutch Nationwide Excessive Tech Crime Unit (NHTCU) reached out to ESET after they’d discovered Ebury on the server of a sufferer of cryptocurrency theft. Working collectively, we gained nice visibility into the latest actions of the group and the malware it makes use of.
Ebury, Ebury in all places
This paper reveals new strategies used to propagate Ebury to new servers. Determine 2 summarizes the strategies we might doc.
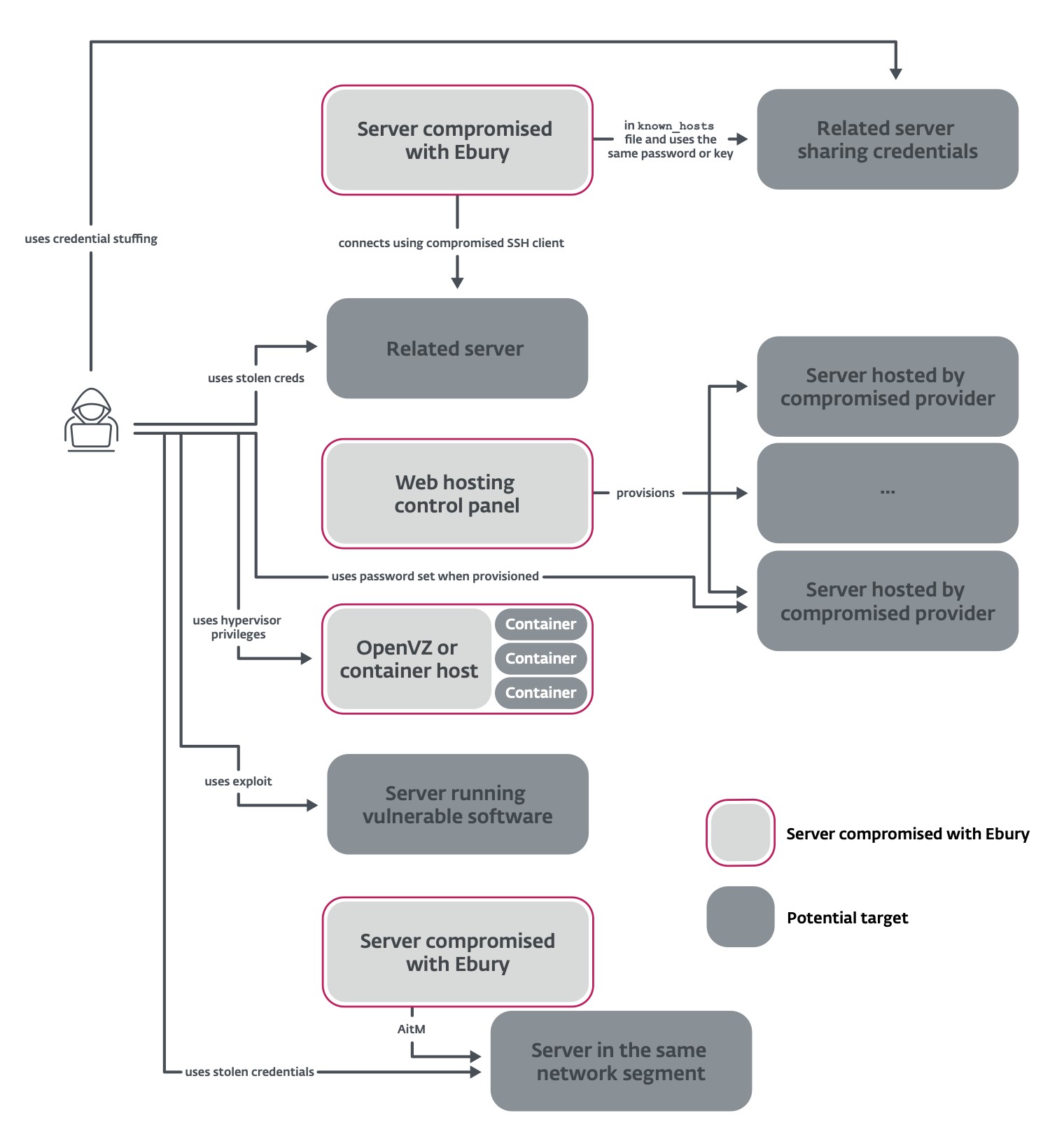
Among the many victims are many internet hosting suppliers. The gang leverages its entry to the internet hosting supplier’s infrastructure to put in Ebury on all of the servers which might be being rented by that supplier. As an experiment, we rented a digital server from one of many compromised internet hosting suppliers: Ebury was put in on our server inside seven days.
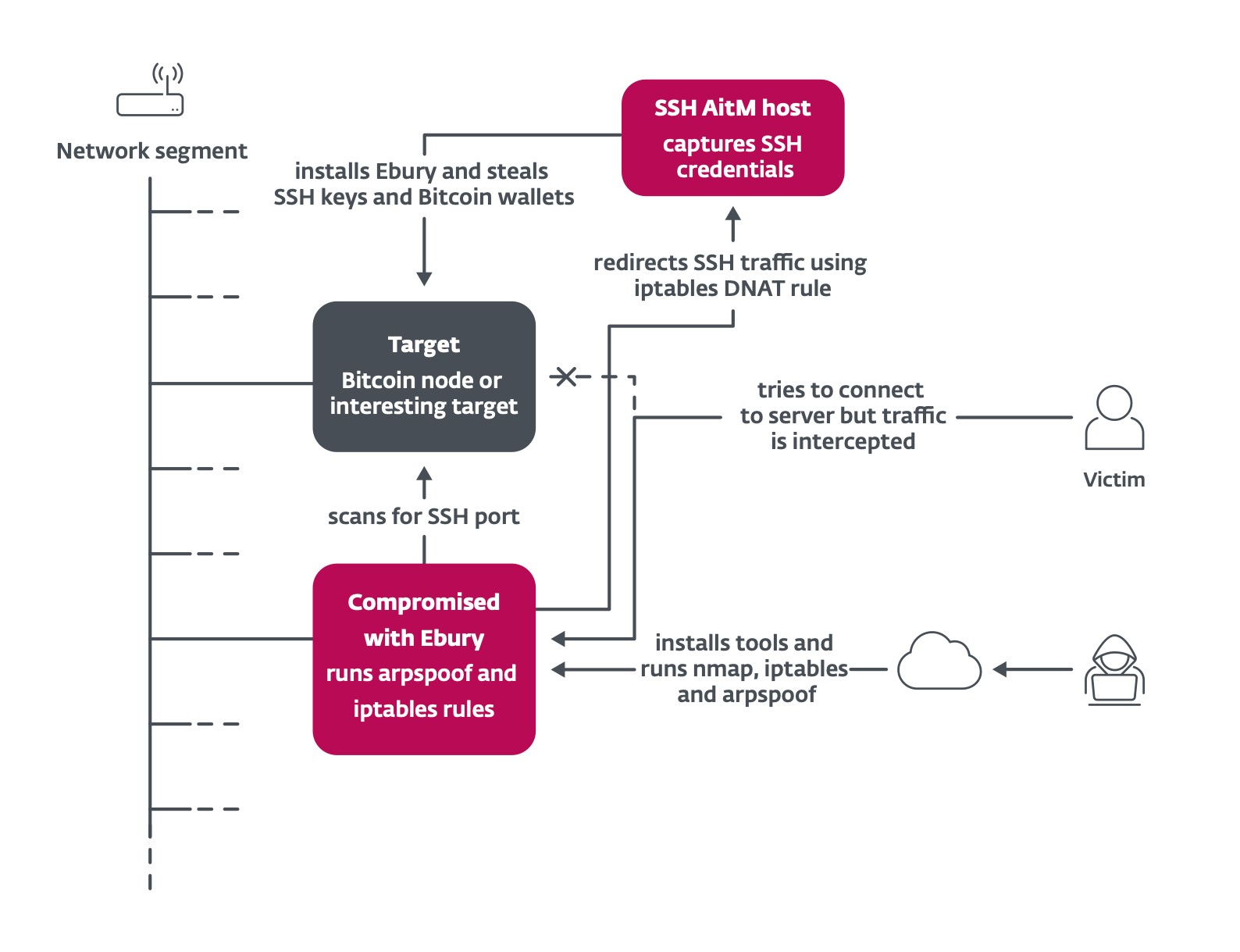
One other attention-grabbing methodology is the usage of adversary within the center to intercept SSH visitors of attention-grabbing targets inside knowledge facilities and redirect it to a server used to seize credentials, as summarized in Determine 3. Ebury operators leverage present Ebury-compromised servers in the identical community phase as their goal to carry out ARP spoofing. In response to web telemetry, greater than 200 servers had been focused in 2023. Among the many targets are Bitcoin and Ethereum nodes. Ebury robotically steals cryptocurrency wallets hosted on the focused server as soon as the sufferer sorts the password to log into it.
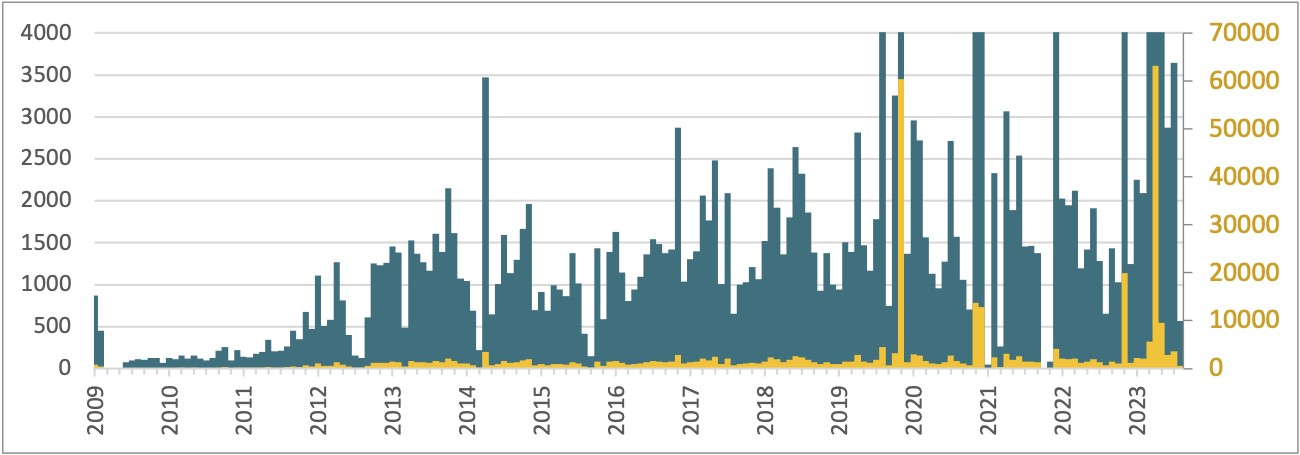
So how efficient are all these strategies? Mixed, about 400,000 servers have been compromised by Ebury since 2009, and greater than 100,000 had been nonetheless compromised as of late 2023. The perpetrators hold monitor of the programs they compromised, and we used that knowledge to attract a timeline of the variety of new servers added to the botnet every month (Determine 4). It’s proven utilizing two scales, to display a few of the main incidents the place Ebury was deployed on tens of hundreds of servers directly.
Monetization
This new paper uncovers new malware households used to leverage the Ebury botnet (Determine 5). Along with spam and internet visitors redirection which might be nonetheless perpetrated by the gang, HTTP POST requests made to, and from, the servers are leveraged to steal monetary particulars from transactional web sites.
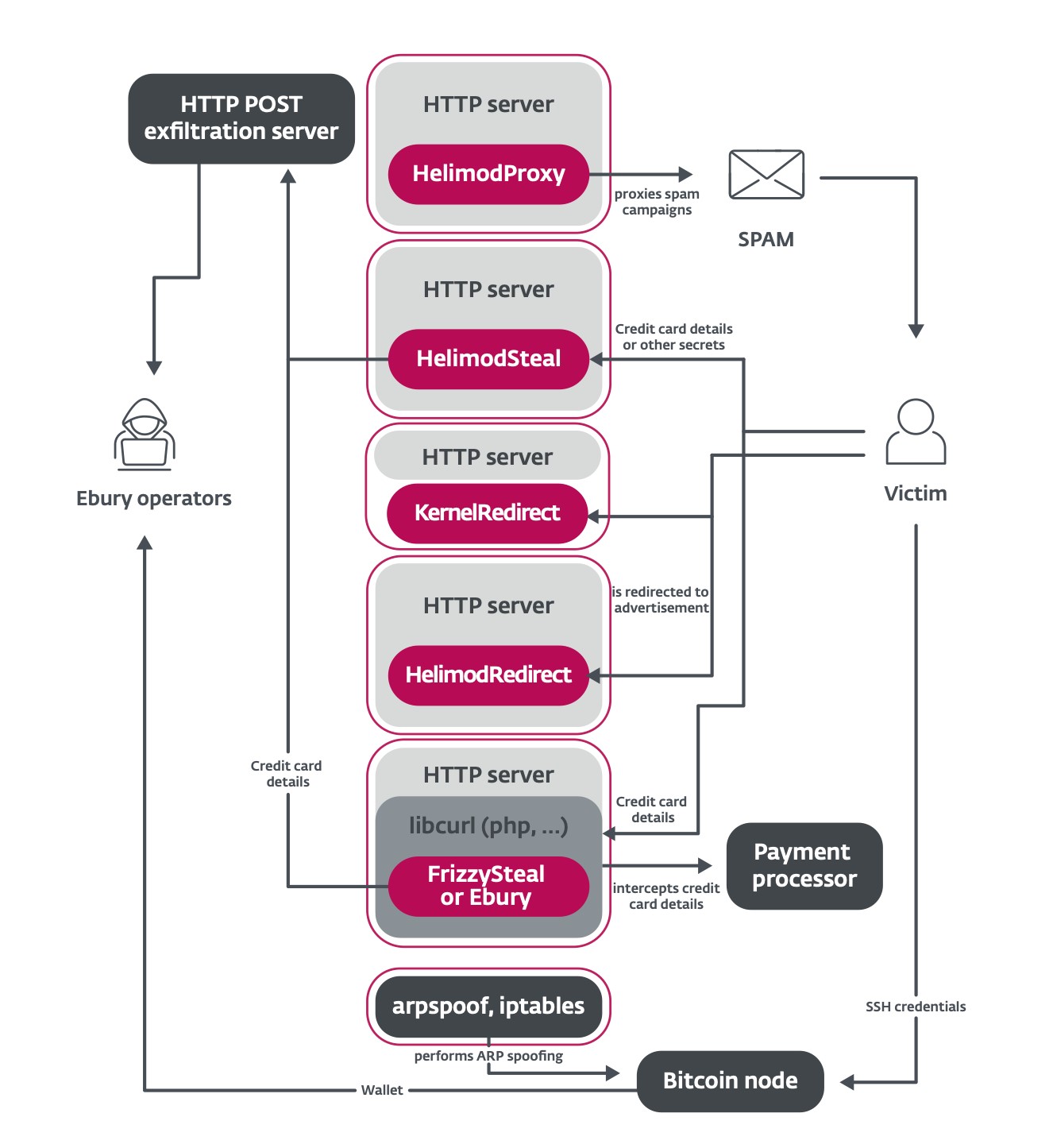
Hiding deeper
The Ebury malware household itself has additionally been up to date. The brand new main model replace, 1.8, was first seen in late 2023. Among the many updates are new obfuscation methods, a brand new area era algorithm (DGA), and enhancements within the userland rootkit utilized by Ebury to cover itself from system directors. When energetic, the method, the file, the socket, and even the mapped reminiscence (Determine 6) are hidden.
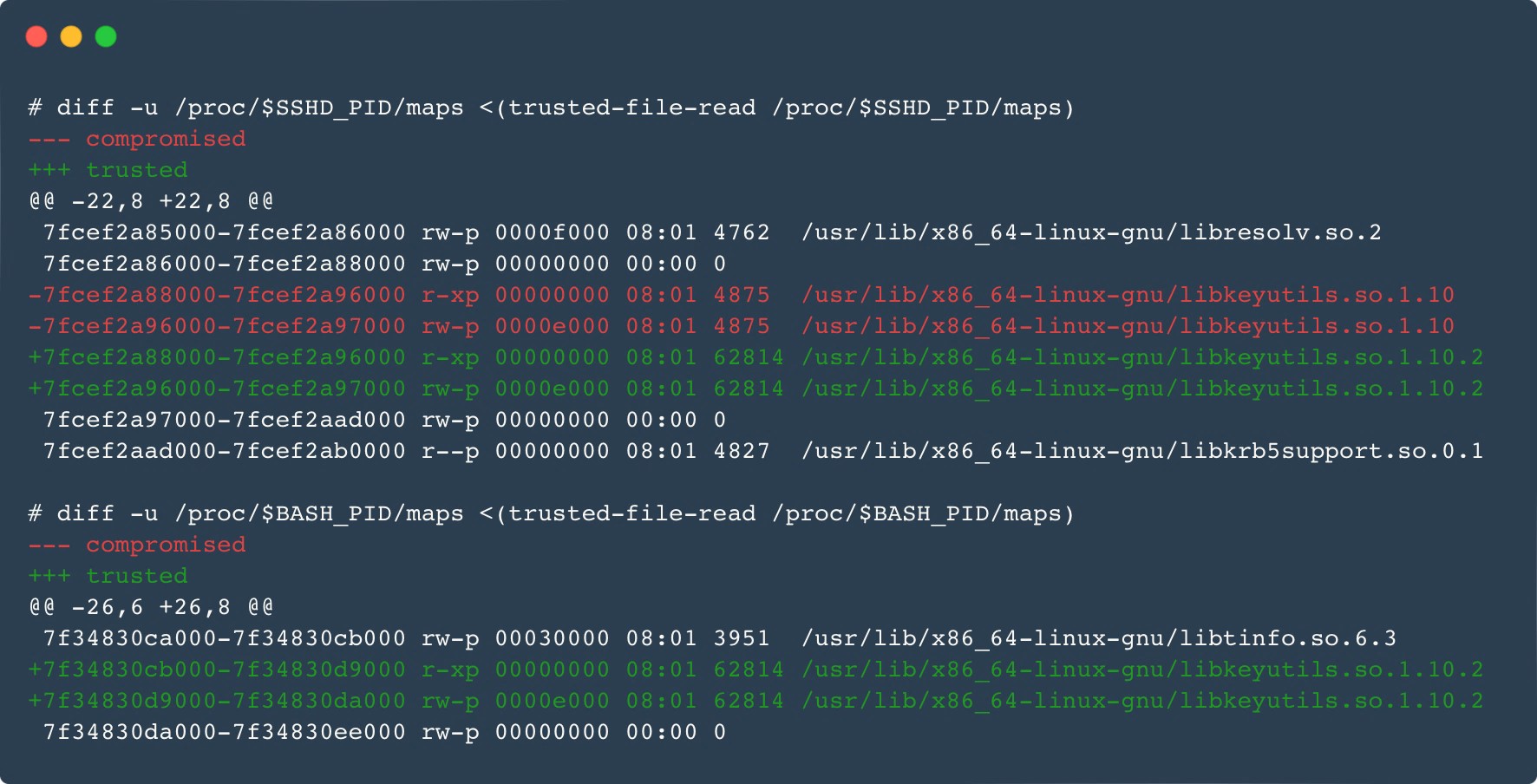
Need to know extra? Am I compromised?
The brand new paper, Ebury is alive however unseen: 400k Linux servers compromised for cryptocurrency theft and monetary achieve, goes into extra particulars about every of Ebury’s features, together with many technical specifics.
Indicators of compromise are additionally out there in ESET’s malware-ioc GitHub repository, and a detection script is within the malware-research repository.
For any inquiries about our analysis printed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at [email protected]ESET Analysis presents non-public APT intelligence stories and knowledge feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Menace Intelligence web page.


